What is Business Relationship Management?
The business relationship manager (BRM) is a senior-level, strategic business partner who shares a crucial link between a Service Providers( IT, HR, finance..) and the Business Partner (Marketing, Sales, Production, Purchase .. ) acting as a connector, orchestrator, and navigator between the service provider and one or more business units.
This is achieved by stimulating, surfacing, and shaping demand for capabilities and assets, in addition to ensuring that the potential business value from those capabilities and assets are captured, optimized and recognized.
While CRM most often refers to a company’s external customers, the BRM typically deals with a company’s internal business partners or an internal provider’s products and/or services.
Whether it be IT, HR, finance, sales, legal, or external, a BRM’s primary objective is to break down the silos separating business functions to optimize cohesive organizational effectiveness and jointly determine strategic direction.
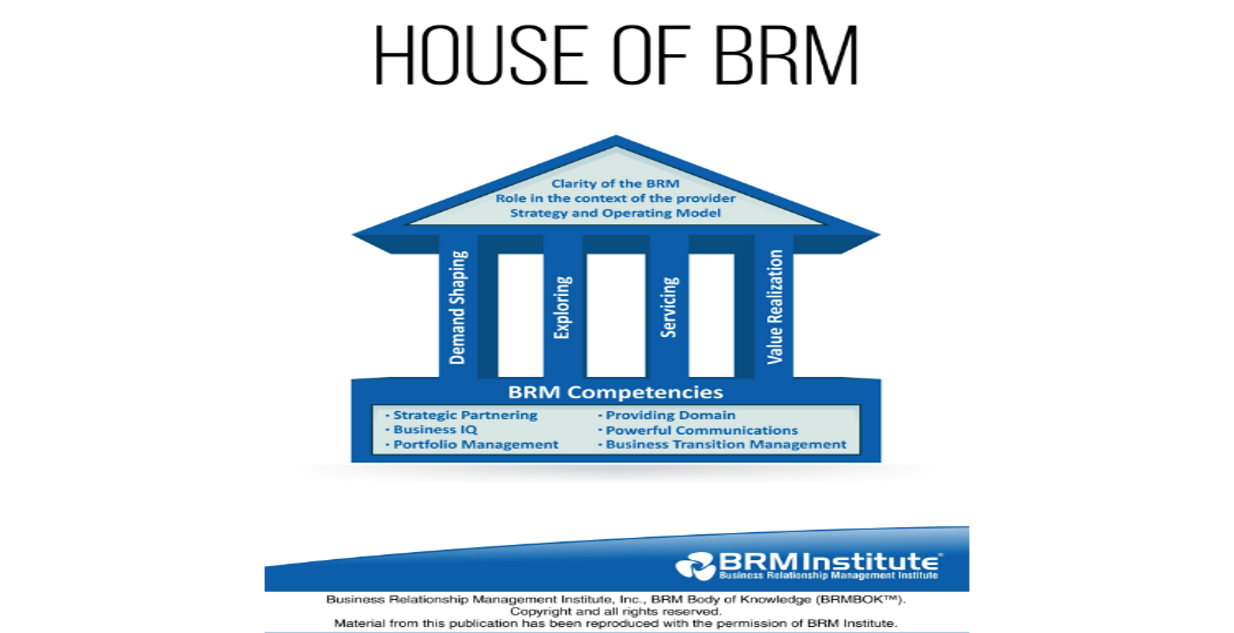
The House of BRM(Image at the top) illustrates three key aspects of Business Relationship Management:
- The “foundation” supports the BRM role and ensures it has the competencies to be effective and deliver value to both the provider organization and its business partners.
- The “pillars” define the BRM space in terms of Core BRM Disciplines: Demand Shaping, Exploring, Servicing and Value Harvesting.
- The “roof” of the House of BRM protects Business Relationship Management as a key aspect of provider capability. It does this by ensuring clarity around how the role, discipline and organizational capability of Business Relationship Management in the context of the Provider Strategy and Operating Model.
These competencies can be leveraged through organizational roles (e.g. in an IT organization, the CIO typically has a role of BRM for the enterprise), a discipline (e.g. all business partner facing service provider roles should be skilled in Business Relationship Management), and an organizational capability (e.g. a service provider organization should be effective in shaping and channelling demand to the highest business value opportunities).

BRM competencies define the skills, traits, and behavior of successful individuals in the role:
- Strategic partnering: Building credibility and partnerships
- Business IQ: Growing knowledge and understanding of the business partner
- Portfolio management: Value realization from products, services, interactions, assets, and capabilities
- Provider domain: Optimization of service management
- Powerful communications: Conveying intention for mutual understanding of risk and reward
- Business transition management: Managing process improvements and enabling new business capabilities
Four Core Disciplines
- Demand Shaping – Stimulates, surfaces and shapes business demand for provider services, capabilities, and products. It ensures that business strategies fully leverage provider capabilities and that the provider service portfolio and capabilities enable business strategies.
- Exploring – Identifies and rationalizes demand. Business Relationship Management helps sense business and technology trends to facilitate discovery and demand identification. Exploring is an iterative and ongoing process that facilitates the review of new business, industry and technology insights with a potential to create value for the business environment. The key benefit of this discipline is the identification of business value initiatives that will become part of the provider portfolio of services, capabilities, and products.
- Servicing – Coordinates resources manage Business Partner expectations and integrate activities in accordance with the business partner-provider partnership. It ensures that business partner-provider engagement translates demand into effective supply requirements. Servicing facilitates business strategy, Business Capability Roadmapping, portfolio and program management.
- Value Harvesting – Ensures success of business change initiatives that result from the exploring and servicing engagements. Value harvesting includes activities to track and review performance, identify ways to increase the business value from business-provider initiatives and services, and initiates feedback that triggers continuous improvement cycles. This process provides stakeholders with insights into the results of business change and initiatives
While BRMs come from all areas of business, the position requires a specific set of skills. including strong communication, strategic thinking, and influential relationship-building. They work to identify ways in which the BRM’s function can support and advance business objectives
Additionally, the BRM shapes business demand into supply by:
- Partnering with appropriate resources to facilitate the creation of idea documents, business cases, and value plans;
- Ensuring value optimization and communication; and
- Enabling continuous improvement in all areas and people around them.
In the end as a BRM, you are creating a culture of ownership, as opposed to accountability.