Design Thinking for Digital Disruptive world and Business Relationship Management
Most of the C-Level executives admit that in today’s digitally disruptive world “what got you here will not get you there … “. So, they are in need of a fresh pair of eyes to drive past this. Traditional models are not relevant any more, including project management, considering IT as Cost centres, organizational structures, roles, and stand-alone frameworks.
In the age of software, the methods that served us well for over a century are truly coming to an end. Capabilities Road mapping based on the Customer Design Thinking is a powerful exercise where Business Relationship Managers and Business Partner Enabling team should jointly work and ensure that IT and other Shared service providers like HR, Finance and Legal deliver value to the business.
BRMs help with perceived value and see things through the eyes of the business partners. Business Relationship Managers are seen as Strategic Partners, Problem solvers and great communicators.
“We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them” – Albert Einstein
In these two-part series we will look into Design Thinking and see how BRM helps foster value through Design Thinking
Design Thinking – A Human Centred Approach
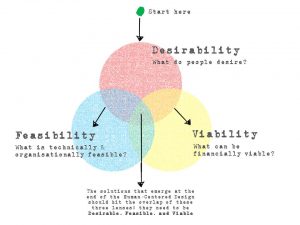 Design thinking helps you with empathy and identify the articulated needs of the client. Creative mindset can be a powerful tool to unearth new ideas and for looking beyond the status quo.
Design thinking helps you with empathy and identify the articulated needs of the client. Creative mindset can be a powerful tool to unearth new ideas and for looking beyond the status quo.
Approaching challenges from a human centred perspective can yield some of the richest opportunities for change.
Every Innovation program has three factors – Technical, Business and People
Technical factors talk about feasibility, Business factors talks about economic viability, and the third element people talks about understanding human needs.
Seeking the sweet spot of feasibility, viability and desirability by taking into account the real needs and desires of customers is what IDEO calls as “Design Thinking”
Design thinking Phases
The five phases of Design Thinking are as follows:
Empathise – with your users
Define – your users’ needs, their problem, and your insights
Ideate – by challenging assumptions and creating ideas for innovative solutions
Prototype – to start creating solutions
Test – solutions
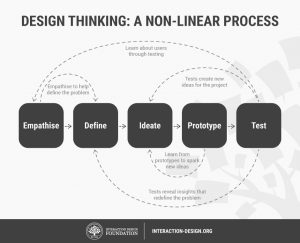
These phases or not sequential. It’s an iterative process and helps us observe and develop empathy with the target users.
We humans naturally develop patterns and are hemmed with timidity, perfectionism and commonly accessed knowledge. This could help us in similar or familiar situations, but they also have the potential to prevent us from developing new ways of seeing, understanding and solving problems.
We humans work with self imposes constraints. Design thinking enables “Outside the Box” thinking and provides a solution-based approach to solving problems.
Convergent and Divergent Thinking
Psychologist Richard Nisbett, who has studied westerners and easterners approaches to solve problem has gone far as to suggest there is a “geography of thought”. He says Everybody is capable of both Convergent and Divergent thinking, depending on the situation.
Convergent thinking is about taking series of inputs, analyse them, and then converge upon a single answer. On the other hand, the objective of divergent thinking is to multiply options to create choices. Divergent thinking helps with solving daunting, complex challenges by articulating ideas that are new and useful.
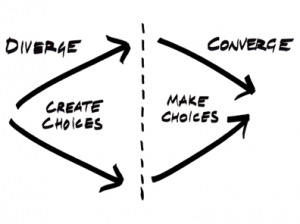 Design thinkers works in a rhythmic exchange between the divergent and convergent phases, with each subsequent iteration more detailed than the previous ones. It’s coming up with new options and the eliminate options and make choice.
Design thinkers works in a rhythmic exchange between the divergent and convergent phases, with each subsequent iteration more detailed than the previous ones. It’s coming up with new options and the eliminate options and make choice.
Conclusion
Companies like Apple, Google, Amazon are making billions by recognizing the value of integrating “design thinking” into their process. Design Thinking is a human centred approach to innovation that helps with understanding the unarticulated or unmet needs of the Business Partner or Clients.
Without embracing constraints design thinking can’t happen. Constraints can be visualized in terms of these three overlapping criteria: It integrates the needs of people (Desirability), the possibilities of technology (Feasibility), and the requirements for business success (Viability).
It’s an Iterative process in which knowledge is constantly being questioned and helps digging deeper. By applying convergent and divergent thinking we will be able to generate multiple new ideas and come up with a solution that meets the business partner to stay competitive.
In the second part of this series we will dwell into what value Business Relationship Manager brings in to Innovate through design thinking and deliver business value in the digitally disruptive world. We will see how BRMs apply Exploring, and Demand Shaping disciplines along with design thinking and enable Value Harvesting.





